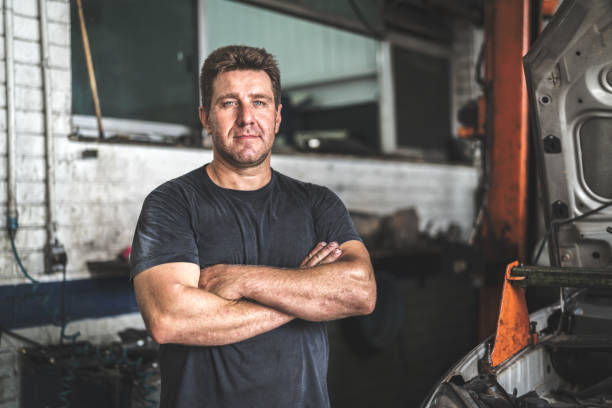
Motor oil is a multifunctional liquid which is used as a lubricant for the mobile engine parts. In addition, the oil absorts excess heat, neutralizes the acid environment in the engine, removes the by-products of combustion in the engine.
None of the working fluids will cause harm such as spent oil in case of late replacement
None of the working fluids would cause harm such as spent oil in case of late replacement. The frequency of engine oil changes directly depends on the engine service life.

Motor oil classification
There are several types of motor oils, they are different in composition (and by properties respectively):
- Minerals (such oils consist of refined oil products, their boiling point in the area of 300 degrees; currently no such oils are used because their capabilities are not sufficient for modern car engines)
- semi-integral (by composition: oil products + synthetic additives; such oil has a large, compared to mineral oils, boiling point-400 degrees, less flammable)
- Synthetic oils (80% synthetic oils consist of artificial oils and additives, boiling point near 600 ° C).
The higher the boiling point, the less oil burns, the excess heat absorption absores, the oil needs to be changed less frequently
The fundamental difference between the three species is in boiling point. The higher the boiling point, the less oil burns, the more excess heat absorption-such oil needs to be changed less frequently.
Another important parameter for motor oil is its viscosity. I mean, the temperature range in which the oil can change its viscosity. The fact is that the oil should not be too viscous for cold start and, conversely, it should not be too liquid to operate at high temperatures. To measure this operating range, the viscosity label was introduced. For example, the index of mineral oils-90-95, and synthetic oils-up to 200.
General recommendations on the frequency of oil replacement
There is no exact oil life. The frequency of oil change depends on many factors: volume, power and design features of the engine; vehicle operation conditions; fuel quality; driving style; and many other factors.
To determine the oil replacement interval, you can proceed using the following algorithm:
- examine the recommendations of the car manufacturer,
- to take into account the age of the car (the older the car and the more mileage, the more you need to change the oil),
- draw attention to the recommendations of the manufacturer of oils which specify the interval between substituting (depending on the type of oil, it may differ),
- to analyse the operating conditions of the vehicle.
The frequency of the replacement of the oil depends on how often the car is used. If a car is used, for example, once a week, the replacement interval is recommended to be reduced because the engine generates an condensation that creates an acidic environment in which the engine loses its properties faster.
Regular short trips also shorten the replacement interval. This is because the engine is unable to warm up to the operating temperature, the load on it increases, respectively, the oil loses its properties faster.
Traffic in traffic jams and fuel-efficient fuels also affect the properties of motor oil. If the vehicle is operated on every day in dense urban traffic, then the load on its engine is increasing significantly, especially in the case of low-quality fuel. In this case, the oil replacement interval should be reduced slightly to extend the lifetime of the engine.
The regular replacement of oil is a very important moment in the life of the car. Of course, it is not worth saving or delaying. It is important to pay attention to the recommendations on oil replacement and its parameters. The manufacturer takes into account the possible operating conditions of the car and calculates the optimal replacement interval.









