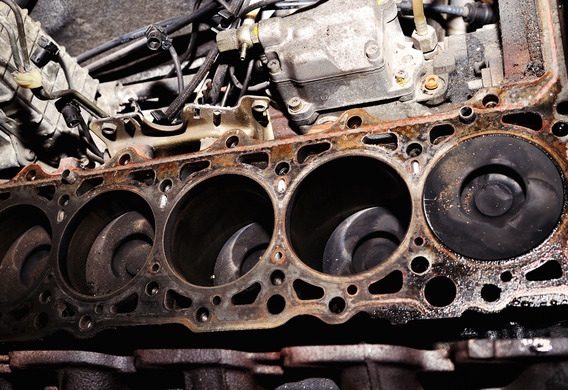
The cylinder block is the main part of the internal combustion engine. The cylinder block serves as a support for the movable parts of the cryopsitic mechanism, attached to it by certain attachments, such as the starter, the generator, and so on.
V6 was first used by the German inventor Gottb Daimler in his car
The cylinder block is the largest corpulic component of any engine with two or more cylinders. Because the block has to be durable and strong, it is poured out of the metal. Generally, iron or aluminium is used. Cylinders of the cast-iron block are crushed into the thicker metal of the hole, and in aluminum blocks steel casings are inserted into them. In cylinders, the pistons are moved, transferring the energy of the expanding gases after the combustion of the gas to the crankshaft, which converts this energy into a rotational movement.
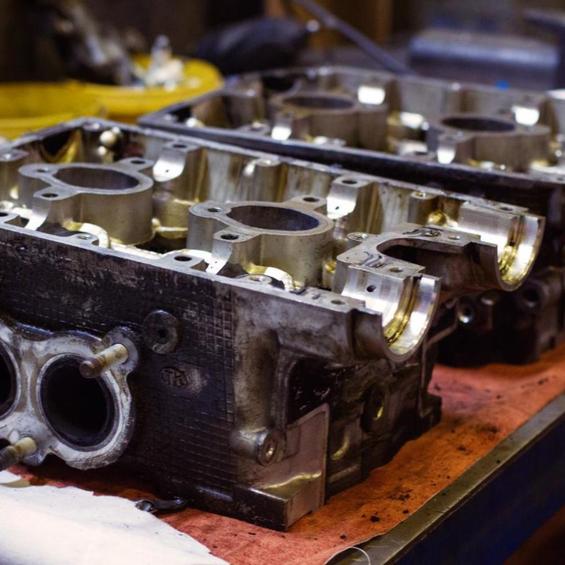

History of cylinder block creation
At the end of the nineteenth century, the cylinder block has undergone a long evolution before remaining as it is used in the design of the vast majority of modern motors.
In order to put a six-cylinder engine under the hood of the little VW Golf, Volkswagen remembered the unpopular design of the VR6 cylinder block
The history of the first cylinder block is connected to the German inventor, Nikolaus August Otto, who invented the most effective petrol engine for his time.
A V-shaped block was invented in 1889 by the Daimler for the construction of an advanced four-stroke two-cylinder engine.
Engine cylinder block design
Cylinders have different designs and configurations of varying complexity. A block can be a straight line, with a sequence of cylinders, V-shaped with different angles, or even consisting of two V-blocks like a Bugatti Veyron EB 16.4. There is a design of blocks at the angle of 180 degrees, for so-called oppositing engines such as the Subaru.
There are blocks of type "VR" in which the cylinders are in a sequential order, serially, but at the same time inclined to one of the two sides as a V-shaped engine. This synthesis of the two varieties in one unit allows to improve its cooling and lift capacity at a low volume. This technology is used in modern engines by Volkswagen. Many owners of Passat, Corr, Golf, Vento, Jetta, Sharan do not even know that they have a VR engine, since the block is covered with a common head and is linked in such a way that the cylinder tilt is not thrown in the eye.
The more cylinders in the block, the greater the engine weight. Therefore, the number of cylinders is limited
When casting a straight line in the cylinder block, there are channels for circulation of the coolant and the oil feed. On top of the cylinder block, the head of the unit is mounted, and the bottom of the crankcase is attached. In addition, the cylinder block serves as a basis for the post-connection of the PPC and of all hinged equipment: the generator, the starter, the carburettor, etc.
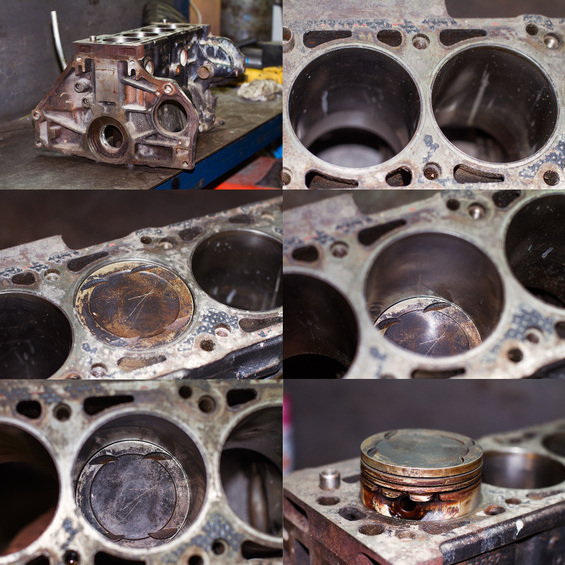

The described engine design with a separate unit and head is the result of a long evolution. Previously, the block was given more functions and what is now in the head of the block was placed in it itself. In the relatively recent engines, a distribution shaft was located in the unit, and in earlier designs there was also a valve mechanism. The head of the cylinder block in the so-called lower-valve engines performed the simple role of the cover with the spark plugs. Possible number of cylinders in the block
Possible number of cylinders in the block
The number of cylinders is very important and can range from 1 to 16. The design increase in the number of cylinders is discussed by the desire of engineers to increase engine power.
If the engine power is not increased by not increasing the number of cylinders, it is necessary to increase the diameter of the piston and to make the larger block of the engine more massive, leading to an increase in mass of the vehicle and the increase in fuel consumption. It turns out that, by increasing the power of the engine, we get lost in mass, which means, in the dynamics, and we need to increase the power again. It's a typical vicious circle.
The Zaporizhzsa cylinder block was executed from an expensive aviation aluminum alloy
Engineers have decided to increase capacity by increasing the number of cylinders in the engine block. The pistons are reduced in diameter, reducing friction losses, which means that the engine power is increasing.
Cylinders
Today we manufacture iron, aluminium and magnesium blocks of cylinders with the addition of different alloys.
The choice of material is due to its inherent properties. For example, a unit of cast iron is the strongest, more suitable for the advance, and less other sensitive to overheating.
The magnet alloy blocks combine the hardness of the iron and the ease of aluminium, but as the magnesium of the rareds and roads, it is used mainly for the auto-port. Surprisingly, a Zaporizhzza crater was carried out with iron or aluminium cylinders of the ML-5 air magnet.
Aluminium units have low weight and good cooling capacity, but require the reinforcement of cylinders. If the aluminium cylinder is to be inserted from steel or cast iron, the walls will wear out very quickly. It is not possible to apply aluminium for the manufacture of pistons as they are immediately attached to the mirror of the cylinder, and the engine will fire.
The cylinder blocks of some BMW models are not amenable to remontov, because the interior walls of the cylinders are coated with a non-renewable composition-
For these reasons, aluminium blocks in the first phase of their application were equipped with "wet" cases of grey cast iron. However, the poorly mounted "wet" casings from the cast of the cast iron broke the aluminum block quickly, so it was not good for the overting and was sensitive to overheating.
The wet "dry" shell casings came to replace the "wet" shell casings. This technology involves the pressing of thin-core cast-iron or composite shell casings in the body of the unit, where they sit "as influential".
Alternative solutions
There are several alternative solutions to toughening the walls of cylinders using the latest technologies. It is a method of silicon crystals on the inner surface of the cylinder or, for example, the use of finished aluminium-silicon casings of Kolbensschmidt technology.
Another technique called Nicasil involves applying silica carbide crystals to aluminium walls of the cylinder of nickel coating. The technology was mainly used in the engines of expensive sports cars, in particular Formula One cars, which are not reusable capital repairs.









