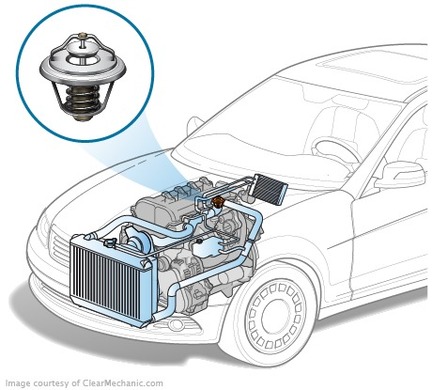
When the temperature is optimized, it must be maintained until the engine is stopped. The thermostat is installed at the "focal point" of the cooling system's path and controls the distribution of the heat from the engine heated liquid. In liquid-cooling systems, two types of thermostats are used: with a solid or liquid filler. Thermostat device with liquid filler
Thermostat device with liquid filler
Thermostat with liquid filler consists of the hull, brass corrugated cylinder, shock, and double valve. The corrugated cylinder is filled with a special liquid with a boiling point of 70 to 75 degrees Celsius. The temperature of the opening of the main thermostat thermostat is indicated on its hull and may vary. For example, motor vehicles in countries with hot climates set thermostats with a minimum valve opening temperature.
The temperature thermostat to maintain the temperature in the chickens was invented by British Cornelius Drebbel in 1620
As long as the engine coolant temperature is lower than the boiling point of the thermostat, the main valve is closed. The cooling-liquid circulation at this time is passing through a small circle, that is, by the engine itself, without falling into the cooling radiator.
When heating the coolant up to 70 to 75 degrees, the liquid contained in the cylinder of the thermostat begins to boil and vaporize. The pressure in the cylinder is increasing, "decompressing" it. Shock moves and opens the valve. The path for the movement of the coolant flow through the radiator is once again.
The Gel Thermostat was invented by Serge Vernier in 1936. Vernet continues to build the thermostats for a variety of cars and these days
When the temperature of the working liquid in the cooling system reaches 90 degrees, the thermostat valve is fully opened. At the same time, its slanted edge has blocked the liquid's access to the small circle.
Thermostat device with a solid filler
In modern refrigeration systems, the most common two-valve thermostats with a solid filler was obtained.
This thermostat consists of the shell, the two inlet pipes, the output tube, the main and the supplementary valves, the sensitive element.
The thermostat shall be positioned before the inlet of the working liquid in the centrifugal pump and shall be connected to it with the output tube. In this case, the thermostat attached to the thermostat is connected to the BV head and the other to the heat sink.
The sensitive element consists of a copper container, a rubber diaphragm and a rod. Between the diaphragm and the cylinder wall there is a solid filler of the material with a high volumetric expansion coefficient, a mixture of copper powders with cereals or a small crystalline wax.
The wax or paraffin used in the automobile thermostats differs from the usual. Specifics appear in wax as a result of distillation
When the coolant temperature exceeds 80 degrees, the solid filler of the sensitive element starts to melt and increase in volume. He's putting pressure on the straps and he's coming out of the tank. The container starts to move up, closing the additional thermostat valve and cutting off the coolant access to the small circle.
When the liquid reaches a temperature of 94 degrees, the additional valve is closed completely. The main valve in this case remains open and coolant is actively circulating through a large circle through the radiator.
When the coolant temperature falls below 80 degrees due to the decrease in the size of the filler, the main thermostat valve starts to close and the flow of the liquid in the radiator is gradually drying up. The valve starts to open an additional valve by ensuring that the coolant has access to the small circle of circulation.
Thus, the thermostat with the solid filler controls and maintains the optimal working temperature of the engine. This increases the service life of all its parts and nodes.
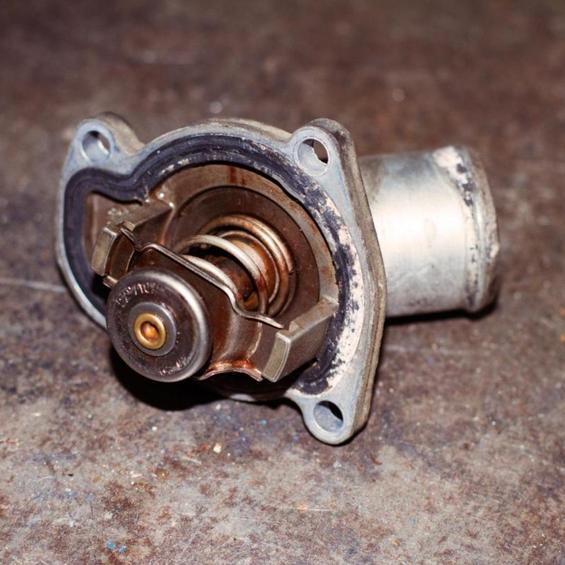

Characteristics of thermostat
The main reason for the failure of the thermostat is the deterioration of its valves.
This may be caused by pollution of the thermostat or chemical degradation of the solid filler.
If the rate of expansion of the solid filler has decreased, this does not mean that the volume has changed. Consequently, there will be no expansion, and the shock will not move, leaving open either one or the second valve. The cooling fluid in the engine will either be heated or overheated.
As a result of the pollution of the thermostat, its valves may be mechanically-mechanically-most often in the open or open position.
Diagnosing such malfunctioning of the thermostat is not difficult. When the engine is cold, the upper radiator tube shall remain cold for some time. If it is warm, then the main thermostat valve is open and the coolant is circulating around a large circle and the engine does not warm up to the optimum operating temperature. This results in the accelerated wear of its parts and components. Engine details are not sufficiently lubricated because the oil remains excessive, resulting in an increase in fuel consumption.
If the thermostat valve is closed in the closed position, the overheating and cooling of the coolant is inevitable, and the overheating threatens to break the engine.
There are situations in which the thermostat failure manifests itself only from time to time, when the valve is "flooded", then functioning normally again. Such a breakdown of the thermostat is dangerous because it is difficult to diagnose.
If the engine is not heated for a long time if the vehicle is not heated badly, if the sensor controlling the temperature of the oJ is in the red zone, check the condition of the thermostat immediately. Any one of these signals might signal a breakdown.









