The De Dion suspension is the only car structure designed by a royal official. Suspension functions
Suspension functions
The suspension can be divided into two groups-dependent and independent. The axis of the dependent suspension axis are tightly linked, while an independent system allows each wheel to act independently, which reduces the inclination of the car body and improves the comfort of its management. The dependent type does not provide these advantages, but it is structurally simpler and cheaper in production.
The De Dion suspension is a compromise that brings together the advantages of a rigid bridge and an independent suspension. This design applies only to the driving axis of the car.
The De Dion system was installed on Volvo 345 1975 and Alfa Romeo 75 1985, as well as the famous Ferrari Testarssa. There are also modern cars equipped with a De Dion suspension, for example, VAZ 2108, Smart, Honda H-RV. On military trucks, the Swiss army is equipped with both axles. Accordingly, the truck is full.
History of creation
The Count of Albert De Dion, whose name is the type of suspension, was the representative of the French aristocracy of the 19th century. This man loved cars and fast driving. Historical data are extremely controversial, and one source asserts that the count has little thought in the car industry and has only financed the company, but there is data according to which he personally designed the construction, and the mechanics epitomized his ideas. The company, led by De Dion, was founded upon the acquaintance of the Count with the engineer Georges Bouton and the mechanic Trepard.
Count Alber was very interested in the steam engine of Buton and offered to finance the development of an engineer. So the light saw the company "De Dion-Bouton", which designed the construction of a four-wheeled vehicle and applied the same type of suspension of De Dion.
The desire to develop such a suspension, which will ensure comfortable movement, can be understood if the attention is paid to the road surface of France of the 19th century. The first car with a steam engine, which the Count managed in person, actually spilled over during the movement, since the bridges were made of stones and were not adapted for driving on the vehicle. It was the idea to connect the wheel of the wheel with the beam, and the gear reductor (the mechanism of the wheels of motion) fixed the attached to the bodywork. The design itself proved to be a very good one, but not for the nineteenth century, since the material of that time was not strong enough.
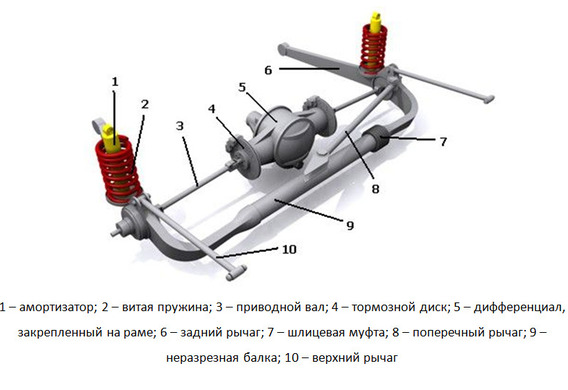
De Dion suspension device
The suspension system, developed by Albert de Dion, is a dependent wheel, the wheels are connected by a whole transverse beam, but it is different from the standard type. The main advantage of such a system is that it provides an opportunity to balance the mass of the vehicle.
For ground transport that has a suspension system, the concept is introduced as a subressored and unbroken mass. The unressored is referred to as the mass of the wheels and other parts that are fasten to them (brake mechanisms, discs, rubber). The subspring is called mass of the remaining parts of the car. The more the subspring mass, the more comfortable the move, stabilter control. A force with which the unbroken components act on the vehicle must be compensated by a subspring mass.
All the elements of the dependent suspension are related to the unbroken mass, and consequently it becomes very difficult and it is not necessary to talk about the comfort of driving. Considering the fact that in the nineteenth century these masses were not known, it can be assumed that the engineers were guided by intuition, but the concept of the suspension of De Dion was to remove the superfluous mass and move it to the body of the car. What has been achieved by securing the gear reducer of the main gear (engine that makes the wheels rotating) to the body of a motor vehicle. In turn, the gearbox gives the wheels rotation with two halves with two hinges on each. Thus, the suspension remained a dependency of the wheels, but the unoccupied mass was reduced to a minimum.
Plus and Minus
All the dependent signs, including De Dion, have one significant negative: the body shell is significantly rocked during heavy dispersion and braking.
Among the pros, you can highlight the ease of installation and the small weight of the construction. Very often, when the manufacturer refuses an independent suspension for any reason, the case of the De Dion type is used.
Since the light saw the system of Alber's graph, it has been a long time and the design has undergone some changes. As a general rule, engineers take advantage of the Deion design, but use modern technologies and materials. This is what was done in the development of the Mercedes R-class and achieved a good balance of manageability and comfort.









