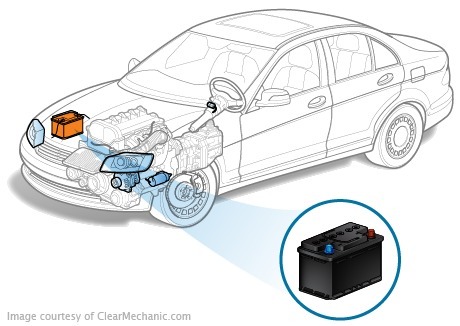
The word "accumulator" in Latin meaning "accumulator" (from accumulo-collects). The battery and generator are electric energy sources of the car. The battery energy is used for the work of the starter, injector, lighting equipment and the engine control unit. A high force that requires a car for full operation, one battery is not to be issued in the force, so the battery usually installs the battery (A), which is a series of accumulators that are connected in series. The power of the current is added together, the output is sufficient to start the engine. Vehicle Battery Vehicle
Vehicle Battery Vehicle
The car battery is a chemical source of current. Depending on the design of the car, it may be under the hood, in the passenger compartment, under the driver's seat, in the boot, etc.
Each battery in the battery is a water-sulphuric acid solution (electrolyte). In technical jargon these tanks are called "banks." It is the quality of the sulphuric acid and water, which are part of the electrolyte, depending on the life of the car battery.
The electrolyte contains electrodes-packages (many positively and negatively charged plates) made of lead alloys. The alloys contain components protecting lead from corrosion. The plates are divided into small cells for active mass. Active mass is the main chemical reasset in the battery.
Positive and negatively charged plates are coupled in pairs with the tanks, which, in turn, come out to the water-clamps (s). The battery terminals shall be connected to them. There are batteries with upper or lateral terminals.

There is a so-called "shlama gap" beneath the plates of the bottom plates. There are chemical reactions (pieces of active mass, lead, etc.). These waste should not pollute the bottom edges of the plates, as otherwise the closure will occur.
There is a separator between the electrodes. This is usually a thin porous leaf in polymer materials, which is set so that no short circuit occurs.
The entire structure is assembled into a bag and is drawn by a bandage that does not allow the plates to be removed, because the plates can be moved under the vibration of the vibrations.
How it works
The principle of battery operation is based on the conversion of chemical energy into an electrical energy. Active substances of electrodes are partially dissoluble under the acid. On the negative electrode, electrons remain on the negative, and the positive electrode (anode) has positively charged lead ions. There is a difference of potential between electrodes (voltage). As a result, the electric current begins to run along the chain.
History of creation
Since the battery was created by the Frenchman Gaston Plante, the principle of work and the design of the device has not changed. This device has been in existence for almost 150 years.
However, it is unlikely that the first battery can be installed on one of the modern car models. The design has been improved over time: the battery was reduced in size, acquiring new qualities. If it used to be used only to start the engine, at present, when the engine is switched off, it provides a variety of electricity consumers. If the engine is switched on, the battery is helping the generator to supply all the vehicles that are using it.
Up to the end of the 1940s, all vehicles were equipped with electrical equipment 6V (this means that the battery had three 2V batteries). Batteries with these voltages are used mainly in the motor vehicle. On all cars, the voltage corresponds to 12V, and only 24V in heavy trucks, trolleybuses, trams and army vehicles.
Types of car batteries
There are four types of car batteries.

1.Serviceable by the CCM. It's classic batteries. Their metal plates contain lead and antimony alloy. This type of battery allows for the replacement (additional) of the electrolyte through the special filler neck. Today, there are practically no serviced batteries.
2. Malicory ACB. The manufacturers realized over time that if the antimony level of the alloy was reduced to a minimum, there was no evaporation of water. The battery has become thin. The main producers are Baren, Varta, Bosch.
3. QA calcium. The plates are made of calcium lead. This is an almost unserved battery, which was first invented and built by the American company Delco Remi.
4. Hybrid (combined) AKB. It is created on the basis of calcium (calcium plates) and alumicus (anodal plates) of alloys. This "mixing" of technology allows for longer life. Today is the most popular type of battery.
One of the most important characteristics of batteries is their energy intensity. This is the amount of electricity that the battery is allocating to the final voltage. Small-length vehicles (Mercedes B200, Fiat Uno 60, Daewoo Matiz, etc.) are also small-about 30-40/h. Motor vehicles with large engine capacity are typically equipped with 100-120 A/ch batteries.
Different types of batteries
All types of batteries have their pros and cons. It's quite difficult to say what the best view is. For example, calcium cells have low self-discharge, do not require any maintenance, but do not tolerate deep bits.
For maintained and low-serviced batteries, the deep discharge is valid, but they require a periodic fill of distilled water.
Battery capacity is reduced with a reduction in temperature. Short trips in frosty weather can reduce even new batteries, which in turn can lead to a reduction in useful life (especially for calcium).
Operational issues
If the battery charge level is 70-90%, it will last a very long time.
The servicing of the CCM is simplified if they have an indicator. A green LED indicates that the battery can be operated, and the battery must be black. If the indicator is white, an electrolyte (distilled water) must be added.
"Unserved" batteries are made in such a way that they do not need to take care of the electrolyte level. But this applies only to a fully functional car. If the relay fails or fails, the battery of any design will be boiling. If the boiling is long, the whole new battery will have to be changed because it will be unsuitable.
You cannot allow deep discharge of the battery.
It is not desirable to replace the battery when the engine is running, because the voltage spikes may cause the car's electrical equipment to be uninhabitable.
It should also be taken into account that the different models of the car and the different location of the battery terminals respectively. Some of the batteries have a plush adhesive on the left, some on the other side. This is what the ACB's polarity depends on. In the case of battery, it is necessary to consider polarity and diameter of the terminals, otherwise the wires may not reach the terminals of the PSC of another polarity.
It must be remembered that there are differences between the bodies of the various members of the CCM. At the cars of Honda, Subaru, Suzuki, Toyota European production, the size of the ACB shell is not in line with the European standard, the terminals have a European standard. These same Japanese and Asian production machines neither shell nor terminals are European.
In addition, the Jeeep, for example, is above and shorter than the European one.
To avoid electrolyte leakage, it is necessary to check periodically that the terminals are secured. If necessary, tighten the nuts. It is also necessary to remove the possible salon and smear them with special plastic lubrication to the poles.







