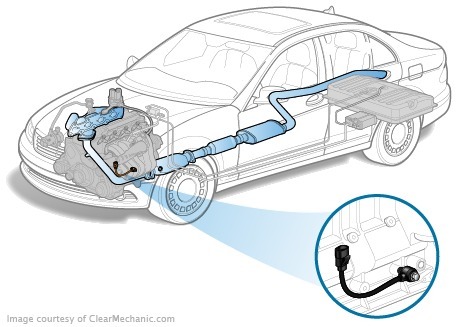
The sensor monitors the detonation of a detonation that is destructive to the engine of the process caused by the incorrect composition of the fuel-air mixture. Principle of detonation sensor
Principle of detonation sensor
The detonation sensor is part of the internal combustion engine injection control. It is the evidence of the detonation sensor that guides the engine control unit when calculating the amount of fuel required for one operating cycle.
What's the harm of the detonation?
Detonation-an excessively rapid explosion, combustion of the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine. The main symptoms of the detonation are the metal cod at the top of the engine, the vibration, the overheating. Detonation is extremely harmful, because due to a sharp increase in temperature in the combustion chamber it is possible to mourn and break the parts of the piston group and valves in the cylinder head.
If the ignition is normal, the air mixture shall only be activated at a certain time of compression. Detonation begins when the fire occurs much earlier, in the middle of the compression cycle. Burndown is the nature of the explosion, as fuel burns in a very short period of time. The characteristic sounds of cylinder explosions are heard in the engine compartment, and the pressure in the cylinders is rapidly increasing. The consequences could be the destruction of the details of the critical mechanism and, above all, the piston group.
How is the detonation going on?
Compressed fuel, the fuel mix is warming up. When the spark pluds between the electrodes, the fuel burns. The burning starts with the electrodes of the candle and then spreads to the outer layers.
On detonation, the combustion front, as in the case of normal operation, extends from the centre to the walls of the cylinder. However, this happens so quickly that the mixture inflammates not uniformly, but the crest of the combustion chamber, and burns almost immediately. The temperature and pressure rise is comparable to the shock wave. The concentration of pressure and temperature occurs in the wave propagation area. When they reached the top of the cylinder wall, the wave collides with them, and at this moment enormous loads are created in the metal. The sound that we hear and consider a symptom of a detonation, and there is a call that occurs when the wave hits the metal sides of the cylinder. Naturally, the cylinder block is capable of absorbating these loads before time, but the piston and the compression rings and the plate of valves will be destroyed quickly enough. In addition, the process is accompanied by a sharp spike in temperature, as a result of which the rings may begin to melt.
Causes of detonation
There are several reasons for detonation. It is most often caused by the use of fuels with a lower octane number. Which fuel is suitable for use in the engine, can be obtained from the instructions to the car. The second reason is the use of poor quality fuel. Fuel producers often use chemical additives to increase the octane number of fuel (and price). This practice is very dangerous for engines, as the fuel is in fact not consistent with its class. Chemical processes may be activated if the combustion chamber is hit by temperature and compression. For example, in the fuel scale in areas where the burning front has not yet reached it, there may be increased concentration of certain substances with explosive properties.
There is always a risk of acquiring dangerous fuel at a gas station, but in most cases the detonation occurs due to misfiring, especially if the spark ignates the mixture too early when the pressure and temperature of the combustion chamber are too high.
There are other reasons. There is, for example, the concept of "fuel resistance". This parameter may be broken in the manufacture of petrol at the plant, and it may change if the engine is too worn and the combustion chamber enters the oil from the crater by mixing it with the fuel and the air.
There is a general rule to keep in mind the owners of all cars. The most affected by the detonation of small volume engines, "dispersed" to "remove" a large number of horsepower. For this purpose, the compression ratio has been increased in their combustion chamber, which means that a situation has been created in which the detonation may be reasonably easy. Fuel with low octane number is not strictly recommended for these engines. Turbo engines are even more susceptible to this phenomenon, where the compression ratio increases as the pressure is increased in the intake system.
How does the sensor help you fight a detonation?
The probe itself, with a detonation, cannot do anything. However, the detonation sensor makes it possible, in a direct sense, to "feel" and quickly transmit the information to the control unit.
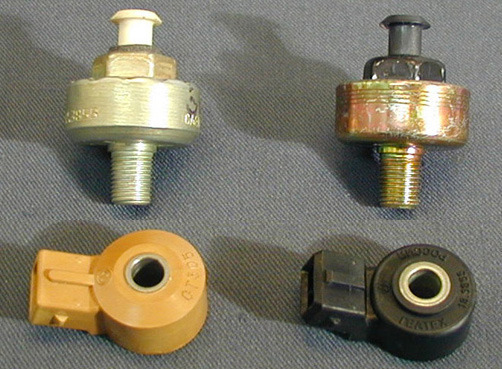
The sensor whose operation is based on piezoeffect is mounted on the cylinder block. In the event of a detonation, the block begins to vibrate. The piezoelectric plate is compressed within the detonation sensor, and there is a difference of electric potential at its ends. The electronic engine control unit interprets the electric signal change as the occurrence of a detonation. In response, the computer adjusts the angle of the ignition to change the combustion parameters of the fuel-air mixture. The programme in the control unit may change the way ahead in a sufficiently wide range, allowing the engine to operate on low-octane fuel or faked fuel. However, each owner must understand that the automatic adjustment of the UAZ has its limits.









