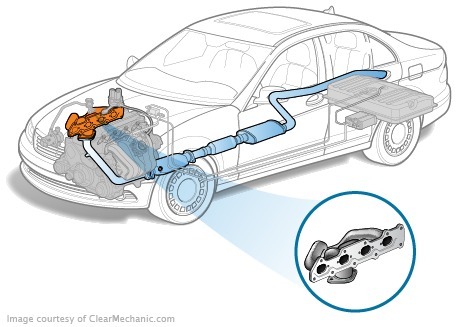
The exhaust manifold is a massive metallic collection for hot gases which are removed from the engine cylinder after the useful work has been performed. In the reservoir, the pulsating exhaust gas flows shall be put together and thrown into the tailpipe of the exhaust system. Exhaust manifold
Exhaust manifold
As a rule, the exhaust manifold is simply a simple piece of iron or stainless steel. Cast sewers usually represent a single piece made by the casting method, as the cast iron is almost impossible to bend. Steel is a more resistant material, so steel manifolds are made from curved tubes by welding. There are short channels in the cast-iron reservoir leading to a single chamber. Cellular collectors are of low efficiency because short channels are unable to accept a large quantity of gases at a time and do not provide the desired level of combustion chamber. Their dignity is low cost and simple production.
The steel collector is covered by a layer of material that prevents the heat from being allocated to the engine compartment
The steel collectors came to the industrial production from the motor port world. The details of this type are usually made of stainless steel, and in the case of the most expensive brand of automobiles, ceramics. The dignity of ceramics is in low thermal conductivity, so the collectors from this material practically do not emit heat into subspace. Pipes by increased channel lengths improve their capacity, and have become more active in recent times. They are more easily optimized by channel pressure and by another parameter.
Process optimization in exhaust manifold
The phenomenon of tube collectors gave an impetus to the development of the exhaust system in unexpected directions. For example, in a number of motorcycle engines Yamaha, the exhaust manifold is equipped with an intelligent reverse pressure control system. This means that there are electronically controlled curtains capable of covering and opening the outlet depending on the operating mode. In this way, the waveform pressure in the exhaust system is aligned and become more or less constant, thus avoiding the formation of curing at a sharp increase in turnover. Many car manufacturers are experimenting with such systems.
Peculiarities of the exhaust manifold for powerful vehicles
Engine collectors with a large number of cylinders are different from the usual mandatory resonator presence. The fact is that the manifoles of such engines are generally divided into two parts. For example, if the engine has 8 cylinders, there will be two parts. The first part is the exhaust gases from the first, second, third and fourth cylinders, and the second part from the fifth to eighth cylinders.
The same-liners of exhaust manifold have come into serial production from the world of sports. Now such details can be seen even in the humble Toyota Yaris
There is a certain order in which the engine is operated: the mixture shall be fuelled in a sequence not in a row but by a certain algorithm. Therefore, there are situations in which exhaust gases fall into one part of the manifold of two and more cylinders in a short period of time and the second part shall not be activated. Naturally, there is a high pressure that the reception pipe cannot take immediately. To reduce it, the two parts of the manifold are combined by a jumper, a resonator that removes the part of the gas to the unaffected part in order to reduce the pressure in the production. Often these engines are equipped with two independent reservoirs and two independent exhaust paths to solve the problem more dramatically. That is why cars with powerful engines often see two exhaust pipes.
Working principle of the exhaust manifold
One side of the collector is attached to the head of the cylinder block where there are windows for exhaust gas from cylinders. On the other hand, a reception pipe is attached to the manifold through the flange connection, or a catalyst, depending on the structure.
The exhaust gases enter the manifold from the combustion chamber, and then shall be reflected from the internal walls and shall be sought back in the combustion chamber. As a result of the gas flow in both directions, the flow of gases in the manifold shall be wave-shaped.
Iron and stainless steel-the best materials for the production of manifolds constantly exposed to the aggressive exhaust environment
However, the main direction of the flow remains unchanged from the engine to the exhaust path, which ensures efficient cleaning of cylinders from combustion products. In the case where the engine is fitted with a turbocharger, the manifold pressure is used to actuate the turbine's retina which is installed immediately after the manifold. In this case, a portion of the exhaust gas is returned to the cylinder through the intake manifold, creating an elevated pressure not reached by direct air capture.
Main causes of problems and repair
The appearance of noise in the engine compartment becomes the first indication of a malfunction of the collector. It is often inoperable in cases of engine overheating when the adjacent plane is curved due to changes in the structure of the metal due to excessive temperature. In this case, there is a gap between it and the head of the block, which is not capable of compensating for the state gasket, and the collector must change. The exhaust manifold is continuously exposed to the aggressive exhaust gases, and after the engine is over, the collector is cooling off, causing condensation that leads to corrosion. Cracks and caverns in the metal that lead to a leakproofness are due to rust. The problem can be solved by welding, but if the process has gone too far, the replacement of the exhaust manifold will be the optimal solution.
It is possible to check the geometry of an adjacent plane of the overheated manifold by simply putting it on a flat table and pressing against the table
When the engine is wet, it is necessary to wait until the exhaust manifold is cooled. Otherwise, the risk of cracking or curvating due to the sharp difference of temperature appears.
Graduation in sports and tuning
In sports cars, the collectors of the tubular type are almost always used because it is precisely in them that the equal length of all the pipes of exhaust gas emitted from all cylinders are mixed at the outlet. In the coprocourse, these collectors are called "spiders" for their characteristic appearance. When the exhaust system is altered, the pipe for "spider" is chosen with a section that exceeds the canals section. This is necessary to ensure that the exhaust gases are not easily released. The steel flush collector enforces a large amount of heat into the subfloor space, and to reduce the temperature on the surface, the inside and outside covers are covered with special pottery spraying or stained with a thermo-resistant paint that performs the same function. With the same purpose, the pipes are wrapped in fabric woven of basalt threads with record low heat conductivity. Due to these measures, exhaust gases are cooled in the following exhaust tracts outside the engine compartment and the engine intake air is lower.







