
Stricter, the term "liquid cooling" is not entirely correct, as the liquid in the cooling system is only intermediate heat transfer that penetrating into the wall of the cylinder block. The role of the transfer agent in the system is played by the air that rotates the radiator, so cooling the modern car is correct to be called hybrid. Liquid cooling system
Liquid cooling system
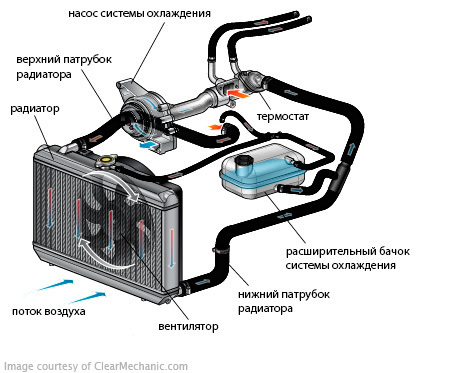
The engine cooling system shall consist of several components. The toughest one is called a "chilling shirt." This is a ramified network of channels in the cylinder block and cylinder head. In addition to the shirt, the system includes a cooling radiator, an expansion reservoir, a water pump, a thermostat, a heat sink fan, metal and rubber connections, sensors and control devices.
Pylon glycoli-the basis of the cooling liquid (anti-freeze) and approved by veterinary physicians
The system is based on the principle of forced circulation, which is provided by the water pump. Due to the constant flow of the hot liquid, the engine is cooled evenly. This explains the use of the system in the vast majority of modern vehicles.
Passing through the channels in the wall of the unit, the liquid is heated and enters the radiator, where the air flow is cooled. When the vehicle is moving, the natural cooling is sufficient to cool the vehicle, and when the vehicle is standing, it is driven by an electric fan, which is activated by a signal from the temperature sensor.
Details of key water cooling elements
Refrigeration Radiator
Radiator is a panel of metal tubes of small diameter, covered to increase the area of heat output by aluminum or copper "feathers". The overall total area of the tape is large enough, which means that the heat sink can be heat radiators per unit of time.
The most vulnerable element of the engine-turbocharger (turbine) design, operating at extremely high speeds. During the overheating, the destruction of the porch and bearing of the shaft was almost inevitable
Thus, the hot liquid inside the radiator circulates immediately over all the numerous thin pipes and cools with enough heat. A safety valve is provided in the filler cap of the radiator, which removes the vapour and excess liquid when heated.
In the radiator of the automatic gearbox, there is a second, independent circuit in which the transmission fluid is cooled.
Broadcrate
The expansion beam is used to compensate for the liquid expansion when the temperature rises. Depending on the design of the system, the tank may be "simple" or "complex". A "simple" bajock is a capacity for collecting excess fluid from the heat of the excess. A rubber tube is attached through the lid and the other end is attached to the top of the radiator.
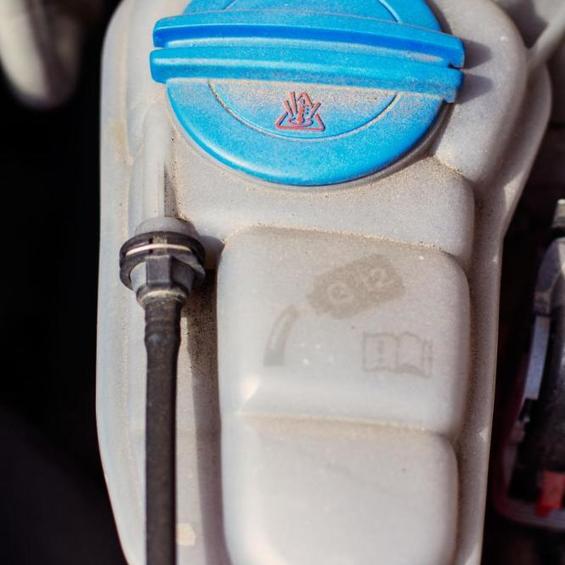

In the more complex version, the tank is a full part of the cooling system. It is under pressure and the return valve is inserted into the tank cover. In this case, the ballpoint shall always have a liquid so that the air does not fall into the radiator when the engine temperature drops. In order to control the wall of the tank pressurized, the label Min and Max shall be marked.
Water pump or pump
The water pump shall circulate the coolant in the system. Typically, this is a centrifugal pump, in which the pressure creates an inside of the center on the central axis with the elbow blades of a complex shape.
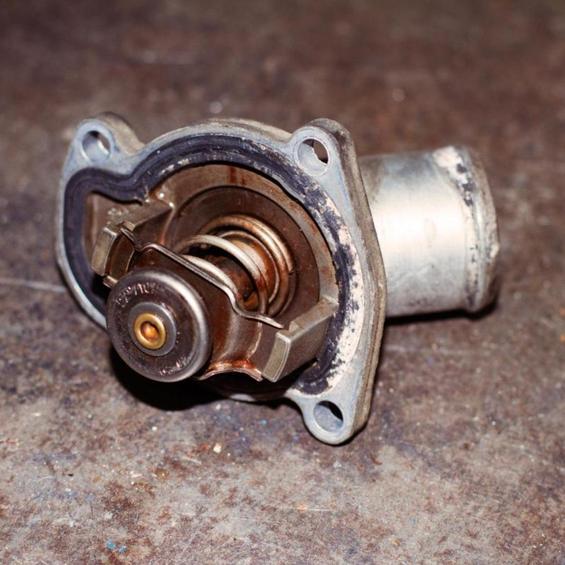
thermostat
Thermostat is a device that maintains a constant temperature in the cylinder block. It does not allow liquids not only to warm the engine, but also to cool it during the winter. It regulates the amount of coolant that passes through the radiator.

Cooling system fan
In some cases, the ambient air flow may not be sufficient for the radiator to be considered efficiently. A fan is provided to ensure the heat dissipation of the vehicle cooling system. In rear-wheel drive vehicles and the longitudinal position of the engine, the mechanical fan is often used, which is driven by a wheel belt from the bezel. The speed of the blades shall be adjusted by the thermomuff (a variety of temples) to which the retina is introduced.
If the fan is attached to the pulleys without thermo-rotation, when the engine is unswerving, more than 3000 revolutions of the wing shall be broken
The electrical fan is used in the front-wheel-drive vehicles (and most rear-wheel drive vehicles). It is connected to the diffuser, which is bolted to the fastening elements along the radiator contour. The advantage of the electric fan is to flexibly manage it with a controller that is controlled by the oJ temperature sensor.
Helper Elements
The liquid cooling system comprises both the electronic control unit, the temperature sensor, etc., and the draining devices for the liquid. The jaweed have to be poured, for example, to repair the engine.
Liquid-cooling system flow chart
Circulation of coolant in the system occurs for small and large circles.
The small circle is involved in the cold start and gives it a rapid progression. Moving in a small circle, the liquid does not pass through the radiator.
When the coolant temperature rises to 80 degrees, the main thermostat valve is opened and the circulation continues in a large circle that includes the heat sink. (Thermostat may be calibrated and under other open temperature).
When the temperature reaches 94 degrees, the additional thermostat control valve is closed, limiting the access of the coolant to the small circle, from the engine to the pump. Thus, the thermostat does not give an overly heated liquid to enter the wall of the cylinder block, preventing overheating.
Depending on the mode of operation of the Armed Forces, the cycle of the coolant cycle may vary. The amount of liquid circulating in each lap depends directly on the extent to which the primary and additional valves of the thermostat are exposed. This scheme provides automatic support for the optimal temperature operation of the engine.
Advantages and disadvantages of the liquid cooling system
The main advantage of liquid cooling is that the cooling of the engine is equivalent to that of the air flow. This is due to the greater heat capacity of the coolant compared to the air.
The cooling system allows to significantly reduce the noise from the running engine by increasing the thickness of the walls of the unit.
The inertia of the system does not allow the engine to be rapidly cooling off. The heated liquid is used to heat the passenger compartment and for preheating of the combustible mixture.
At the same time, the liquid cooling system has a number of drawbacks.
The main drawback is the complexity of the system and the pressure after the warm-up. The pressure-pressure liquid has increased requirements for the leakproofness of all compounds. The situation is complicated by the system's work implying a constant repetition of the heat-cooling cycle. This is harmful for connections and rubber tubes. When the heat is heated, the rubber is enlarged and then compressed on the cold, causing it to flow.
In addition, the complexity and the large number of elements itself is a potential cause of "technogenic disasters" accompanied by a "swimness" of the engine in the event of a failure of one of the key details, such as the thermostat.







