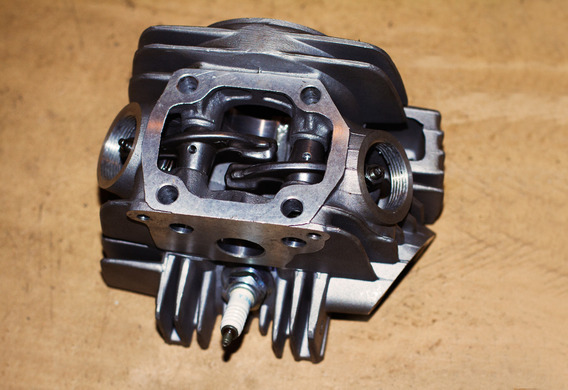
Rockers, or valve cores, are part of the details of the GRM mechanism of some automotive engines, most commonly known as classical construction. In modern engines, after the final transition to the upper allocation of the distribution unit, rockers are rare. Usually, this may be caused by a departure from the standard structure of the valve engine, for example, to reduce the size of the engine. In other words, the engine compartment may be so small that engineers have to change the layout of the engine parts so that the resulting aggregate "fit" into the space.
The engine has been driven by the engine, since the structure of the metal is reinforced by the mechanical impact
rocker device
A structurally a rocker-duplexer lever. At the end of the long shoulder is a tempered cylindrical surface called a boxer. It's the end of the valve.
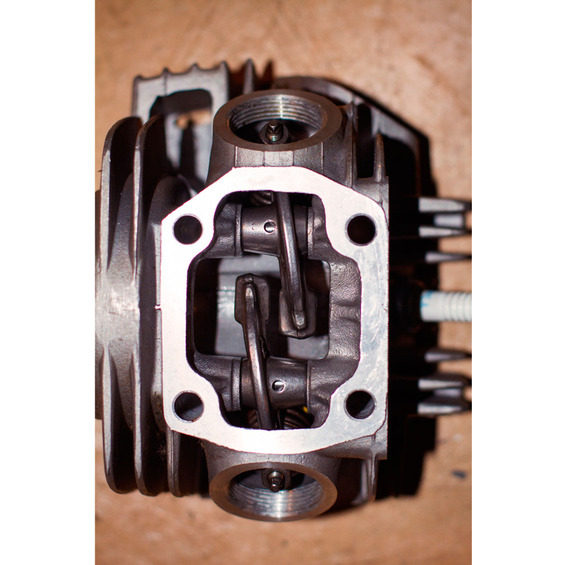

At the end of the short arm of the rocker a bolt is whirlwind to adjust the depth of clearance between the rocker and the valve. The body of the short shoulder is drinted with a hole in the lubricant. Through the adjustment bolt, the lubricant shall pass from the rocker's axis to the top tip of the flap rod of the valve.
Steel-sheet rockers are produced by molding or steel-sheet steel or by casting
The two shoulders of the rocker have a T-cross section. The rockers from the steel sheet are produced by forming or from steel billets by casting or casting. The hoofs are the strongest, they are installed in the accelerated engines.
The axis used to tie the rockers, the floor. The outer surface of the axle is tempering to increase its durability.
The valve rocker or crust is used to transform the forward movement of the pushrod rod up into the forward movement of the valve stem
From the axial displacement, the rocker, situated in the middle between the two pillars of the axle, holds the spiral spring.
How the rocker works
The valve rocker or cracker is used to transform the shaft of a pushrod rod (or pre-valve) into the forward movement of the valve. The trucker was inflating it on one shoulder of the rocker, lifting it up. At this moment the long shoulder is lowered and the pressure of the valve is crushed.
The rockers are located at the top of the cylinder head. The centre of the rocker is the hole in which the axis is presented. The rocker unit's head has been set to each other. The position of the rocker axis is fixed by the two pins pressed into the rack (the support supports are performed in a single unit with the HFC body). However, the structures are different, and the racks can be sideburable.
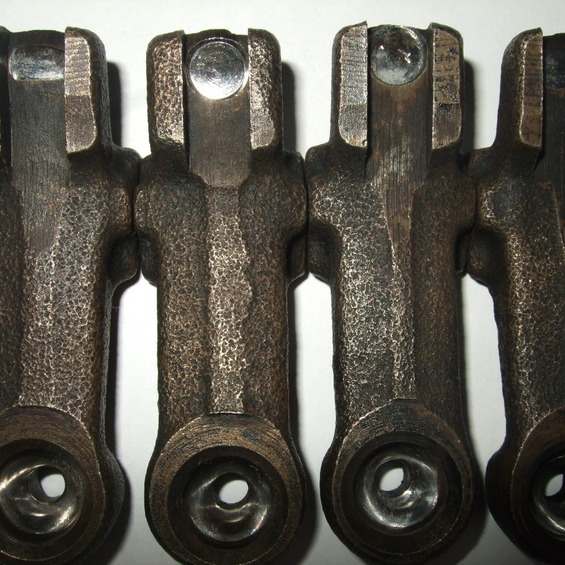

Characteristics of the breakdown
In addition to the levers, the rocker structure consists of tulks that reduce friction and increase the use of the service.
When performing repairs, the rockers shall be thoroughly cleaned and all parts checked, including swelling and bearings for damage and wear. If the damage is not observed, the rockers may be installed into the engine again after cleaning.
The broken rocker entails the failure of the corresponding valve. When the rocker is broken, a knock at the head of the cylinder block appears and the engine power falls.







