Engine cylinder-A processed orifice in the cylinder block that is inside the piston. In the case of a cylinder block made of aluminium, the inboard shall be pressed into the cylinder-casing.
A classic example of a cylinder is a barrel gun. The bullet, like a piston, is moving along its walls under the influence of the energy of the expanding gases
Engines based on a piston in a closed cylindrical box are known from time to time. In this principle, two centuries ago, hot air engines were built, for example, Stirling's engine, or even older thermal machines. In the case of a car, we are familiar with the cylinder as part of the internal combustion engine. However, at least two dozen such engines will be recruited. But despite the obvious differences in appearance and design, they are combined with one common reference part-cylinder. It can be of different shapes, not even cylindrical. However, it is always there.
Cylinder as engine base
In the cylinder, all the essential processes of obtaining and transforming the energy necessary for the movement of the vehicle are taking place. Cylinder, in fact, is the link between two energies: the energy of the combustion of fuel goes into the energy of the movement rotating the crankshaft.
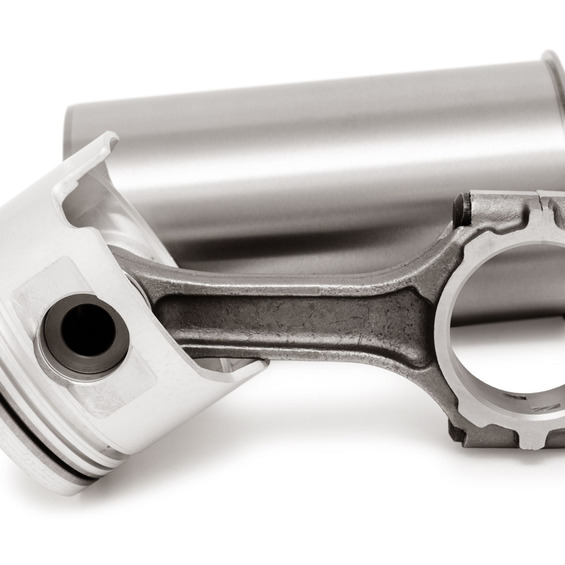

The cylinder is under tremendous pressure in the course of its work. On the one hand it is a high temperature and pressure of expanding gases, on the other hand, high speed of the piston, which reaches 8 meters per second.
The combustion of fuel in cylinders produces such a large amount of thermal energy that the engine has to be cooled even when it is 25 degrees on the street
This process can be compared to a weapon-fired gun, where the powder gas is being pushed in the barrel, (by the way, also in the shape of the cylinder) to a barrel speed of 300 to 1,000 meters per second, depending on the length of the barrel. In addition to the high frequency of 2,500 shots per minute, such as a Venus machine gun.
And if a group of cylinders is to be able to withstand a single record in a sports car, then a typical car from the cylinders requires work for many years, without loss of power, dynamics and other indicators.
Therefore, the engineers of automobile companies have to solve the two main problems related to the reliability of the cylinder-the heat dissipation and the lubricating of the surface along which the piston is moving.
Cylinder design
In the first internal combustion engines, each cylinder was within its own body. This design has continued in our days and is used, for example, in the construction of motorcycle engines. In this case, it is still relevant because air is used to cool the motors open on all sides of the motorcycle. In motor vehicles, all cylinders are combined into a single solid frame, which is referred to as a cylinder block.
For the engine cylinder to be capable of withstanding a high load, it shall be made of solid material-cast iron or special steel with different additives. In order to reduce weight, modern blocks are often made of aluminum. In this case, the interior of the cylinder shall be carried out in the form of a strong steel cartridge, compressed into the block.
The inner surface of the cylinder directly in contact with the moving piston shall be carried out from the metal with special additives to enhance the strength.
The exterior of the cylinder, which is a single unit with a block, is called a shirt. Within the shirt, the cooling liquid circulates through the channels.
In order to relieve the piston within the cylinder, the BMW developers proposed to cover the walls of the cylinder with a special alloy to cover without cartridge casings in the aluminium block
In two-stroke engines, the cylinders have slightly different designs and differ from four-stroke engines by the presence of wind-intake and purged windows. In addition, the lower part of the two-stroke engine has a plate for creating a lower working space under the piston.
Cylinder cooling systems
To remove excess heat from the cylinder of the engine, a cooling system can be provided, which can be either air or liquid.
Air cooling
Air-cooled thylinders from outside are covered with a set of ribs that are considered by oncoming or artificially created by air intakes with a flow of heat from the cylinder.
The fancy drawing on the inner surface of the cylinder is called a henchman, because it uses a [ [ honneal machine]] for its application
hypothermia
For liquid (often called water) cooling, the cylinders are washed by the circulating liquid circulating in the column. The heated cylinders shall be given a portion of the heat of the liquid which will later enter the radiator, cooldown, and again applied to the cylinders.
Cylinder lubricant
The quality of the walls is the second most important problem after the heat dissipation. If the cylinder is not oiled from the inside, the piston is simply wedge, which will lead to the immediate destruction of the engine.
To retain a stable oil-film on the mirror (inner surface) of cylinders, it shall be exposed to the inner lining of the microscrolls. Thanks to the presence of such a mesh there is always a layer of oil that reduces friction (piston-cylinder), dissipates the excess heat and increases the mileage to major repairs.
Non-standard cylinder surfaces
Developers use the latest technologies and materials to enhance the mirror of the cylinder and its durability.
The largest motor vehicle volume is 117 litres. This huge volume is realized in the engine of a career dump with 24 cylinders
Thus, the introduction of silicon crystals in the mirror of the cylinder has repeatedly raised the engine resource, but simultaneously increased the requirements for the quality of the oil and the observance of the temperature. The first engines created using this technology were unserviceable and too expensive. Further developments in this area have made it possible to improve the situation in terms of serviceability. Instead of having to cover the surface of cylinders, which are thicker in the thicker metal, the unit shall be replaced by the assembly of the silicon cartridges to be replaced.
Model technical specifications for car engine cylinders
- Diameter of cylinder
- Height of cylinder
- The working volume is the cylinder capacity from the upper dead point to the lower dead point of the piston.
- The full cylinder capacity is the volume of the combustion chamber and the working volume together.
- The compression ratio is determined by dividing the entire cylinder capacity by the amount of combustion chamber. This criterion shows the number of times a combustible mixture in the cylinder is compressed. Increasing the compression of the cylinder increases the pressure on the piston in the combustion of the fuel, which means that the power of the propulsion system in general is increasing. The increase in this parameter is very beneficial, as it is possible to get a large CPA from the same amount of mixture.









