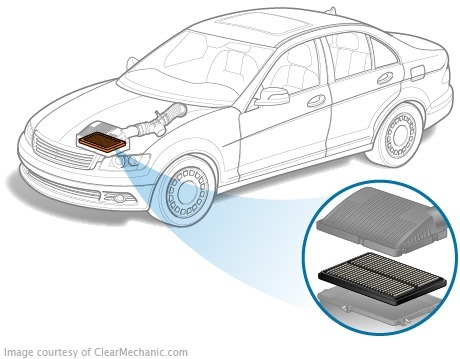
Contrary to popular belief, the engine does not work on gasoline or diesel, but on a mixture of tiny drops of top and air. In order to blend these two components throughout the history of the automotive industry, an entire intricate system of intake has been created. Intake system device
Intake system device
The system consists of several parts, the air and fuel delivery systems, and the manifold where the two components are mixed. As a result of the intake system, the engine shall be supplied with the fuel, the air mixture, which burns practically free from the rest.
The more complex the intake system, the more likely the problem is. This is a convincing proof of the first generation FSI systems from Volkswagen
Each component of the intake system is complex. The air intake system consists of a reception tube determined by the engineers for the engine of this power, the diameter.
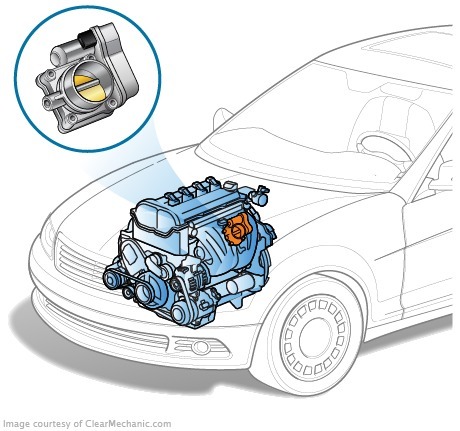
Passing through the tube, the airflow first enters the dosing device-the throttle, and then the measured amount of air enters the intake manifold. The air flow is mixed with the fuel, which comes through the injector walls of the manifold, or centrally, the carburettor's self-assembly. In the most modern designs, direct injection systems are not used and the mixing of the fuel with air occurs directly in cylinders.
In addition to the throttle, direct injection equipment shall be fitted with direct injection engines. They provide a mixing process by separating the air into two intake channels. One channel overlaps the shale, the other through the air is smooth. The intake walls are fitted to the general shaft, which is rotated by means of a vacuum or an electric power train.
The main enemy of the intake system is dust, so the replacement of air filter will never be a useless waste of time and money
Depending on the design of the intake system, the list of components may include turbocharger (far more commonly known as "turbine"), which increases the volume of air entering the engine.

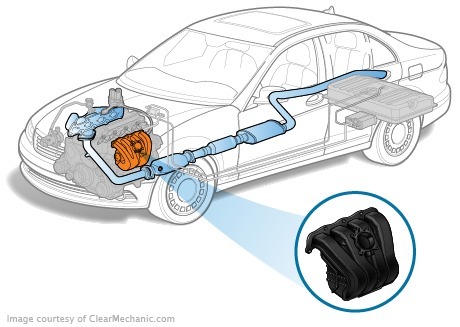
The work of the launch system is closely related to the processes taking place in other car systems: the injection system, waste gas recirculation, fuel vapor capture, and so on. The primary link in this chain is the dilution, which is created in the intake manifold while the engine is running. The vacuum is used as a driving force for the various valve mechanisms of the system for recycling crankcase gases, vacuum amplifier and thp. Inlet-controlled intake system
Inlet-controlled intake system
With the development of microprocessor management systems and the automation of engine processes, the intake system and its interaction with other systems control the engine control unit. The ECU requires measurement data that supply different sensors in real time:
flow-meter (MAF, DMPV, air mass flow sensor);
Intake air temperature sensor;
Inlet manifold pressure sensor;
A throttle position sensor;
With the introduction of the microprocessor control of the engine, the intake system became the "main arena" of battles for optimising fuel consumption
The flow meter and the temperature sensor are needed to determine the required engine load. In some variants of the system, the pressure sensor in the manifold is used instead of the cost-ometer. The throttle position sensor is required to determine the operating mode (spin-up and tch). Depending on the design, there may be additional sensors in the system that are not listed here.
With the development of the automation of processes in the intake system, various executive mechanisms were introduced: the throttle control unit, the intake latch, the shut-off valve of the vapour recovery system, the exhaust gas recirculation system, and so on.

Requirements for fuel-air mixture
The combined work of the throttle and advanced injection engine with the direct injection system provides several types of mixing. The different composition of the mixture is necessary for the operation of the engine in different modes.
A blended mixer is needed to run the engine on a small turn. In this case, the throttle control is fully open for most of the time and intake is closed.
Homogeneic (uniform) blend formation is used for high engine speeds. The degree of opening of the throttle shall be directly dependent on the torque required by the engine. The intake capacity is in the open position.
There is also a mixture (poor homogenous) in which the engine operates at medium speed. The opening of the flap occurs also in relation to the torque and the intake air flaps are closed.
Characteristics of the intake system
The biggest enemy of the intake system is dirt. It may even fall into air ducts protected by high-quality air filters. The filter is made from cotton fabric and needs to be changed as either pollution or regulation. However, the tiniest particles of dirt are able to leak even through the best and the new filter. Falling into the system, dust contributes to the formation of the raid, which makes the operation of mechanical parts more difficult, first of all, the throttle. In addition, dust settles on the sensitive element of the MRI by violating his testimony.
The EGR system perfectly protects the environment, but can become a ruthless killer for the intake system
No less harmful for the operation of the EGR injection system, i.e. exhaust gas recirculation. The system established to protect the environment is often the "killer" of the injection system. In the case of oil from the defective EGR in the intake manifold, it is mixed with dust and enters the combustion chamber, covering all layers of the heist and heat. Therefore, the serviceability of the engine equipped with the recycling system has increased requirements.







