Radiator is one of the main elements of the water cooling system that dissipated in the air the heat from the engine coolant. History of the cooling system
History of the cooling system
It is considered that the first time the radiator concept was applied to the first in 1886 in the free sale of the Benz Velo serial car. In the future, the idea was developed by William Maybach, who invented the cellular radiator and applied it in the structure of Mercedes 35HP. A similar type of refrigerator is used in the refrigeration system and in our days.
There is always a warning on all corks of the radiator, regardless of the car brand, that the radiator is not opened at high anti-freeze temperature
In the earliest cooling systems, the engine was missing a pump or, otherwise, a water pump that ensured the agent's forced circulation (in those days it was normal water). Without a water pump, the coolant fluid was caught in the heat sink with a thermosaic effect. As is known from the physics course, the density of water falls in the spread, and it begins to go up. The water radiated over the top of the tube. In the radiator the water was cooled, and the density of the water radiated into the lower part of the radiator, and came into the engine through the lower tube. However, with the increase in the capacity of the system's cars, the effects of the thermosasila have quickly exhausted due to the low efficiency of the CPA and built systems built on the basis of the centrifugal pump.
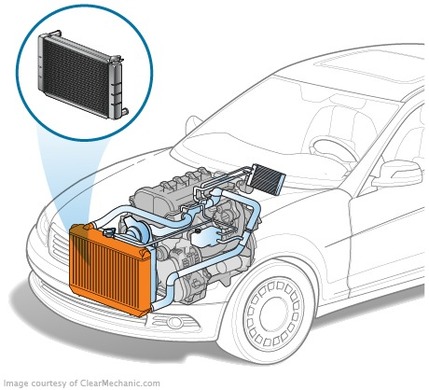
Using the heat sink in the cooling system
The heat sink task is to heat the heat from the engine into the atmosphere, cooling the liquid that passes through it. In order to provide the best heat dissipation, it is usually mounted in the place where it is best considered by a running air flow while the car is moving, behind the radiator grate in the front of the vehicle. Even if the motor of the car is in the rear, the radiator is usually installed at the same location as ordinary cars, and the coolant turning system extends to the engine.
Some cars have blinds in front of the radiator. This device allows to cover the radiator in the winter, reducing the heat dissipation used to heat the passenger compartment
There are alternative installation locations-for example, in the case of the rear engine. The radiator is often installed along the side wall (or along two walls, if the heat sink is two). The flow of the running air shall in such a case be arranged from the air intakes placed in the rear of the vehicle on the side walls of the trunk.
Heat sink design
The radiator consists of two bachts, the top and the bottom radiator, to which the chilling system and the core of the heat exchange unit are attached. The drums are plastic and metal. The core part of the core is a set of seamless, brass or aluminium tubes having a wall thickness of up to 0.15 millimetres, connecting the top and the bottom. Each tube is covered with orem-fine corrugated "harmonica" of copper or aluminum. Aluminium radiators are less than weight radiators, but are destroyed more quickly because of the difficulty of metal welding or mechanical effects. In order to catch up with the heat transfer heat sink, the aluminum radiator must be larger and thicker.
In pre-war vehicles, cellular radiators, made from brass sections of brass tubes, were used. Intra-pipe fluid did not circulate, and cooling was performed exclusively by contact of metal oregation with air.
Cooling liquid temperature setting
The primary function of maintaining a constant temperature in the cooling system is the thermostat that distributes its flow through the contours, which is commonly known as small and large circle. However, in hot weather, when the flow is on a large circle of which the radiator is a part, a fan or several fans, with mechanical transmission (through the templating) or with an electric power train, are used to maintain a constant temperature of the hot liquid to maintain the constant temperature of the liquid.
Alternate heat sink
With the advent of multiple-mode engines, the need for an additional cooling device is needed. Developers of some automobile concerns found a way out in the parallel installation of the additional heat sink with their separate electric fan. The common mistake of the owners is to confuse the additional radiator with the intercooler that is used to cool the air in the turbocharged system. An additional cooling radiator can be seen in the engine compartment of Audi 200 with turbo engine.







