Two main types of turbocharger powered by the exhaust gas stream and a power-driven compressor with a crankshaft drive are used to increase engine power. History of compressor type injection
History of compressor type injection
The idea of setting up the engine to increase engine power is owned by the German engineer Gottlieb Daimler. For the first time, it installed a compressor for its own development car in 1885. The first patent for the original design of the air injection engine for the internal combustion engine was issued in 1902 by Louis Reno.
The turbochargers were used to increase the power of internal combustion engines still in the development phase of this type of technology. In 1911, a turbocharger patented by an American, at the dawn of his development, played a significant role in the military aviation-turbished gasoline engines were placed on fighter jets and bombers to improve their height. The technology has recently been used in automotive dyslexia. The first serial car with a turbo diesel was introduced in 1978. Mercedes-Benz 300 SD, and in 1981 It was followed by VW Turbodiesel. In the future, the use of the mechanical injection device has taken two parallel tracks. The first value was recognized by engineers who were building diesel engines with a high compression ratio and required a forced air injection, that is, two-stroke diesel engines, or where higher unit power is required. The second branch of development is the installation of vehicles to obtain excess capacity.
The history of the automotive industry consists of a large number of types of actuators or compressors. But at present, three types are most commonly used: screw, rotary, and centrifugal. The most traditional use of the injection device for the American and German industries, while the Japanese, for example, tend to use turbochargers.
Differants from turbocharger blower
The injection air and turbocharger shall discharge the same function-pressurized air to the combustion chamber. However, they have a completely different drive design and have a different influence on the nature of the engine operation.
The rotational power of the turbocharger is the flow of engine exhaust gas, and the supercharger is the mechanical power of the crankshaft, which is passed to the crankshaft using the pulley and belt.
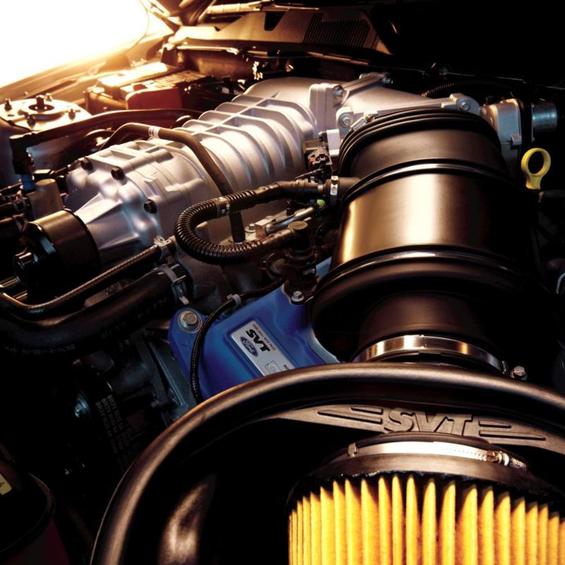

The principle of the increase in power by the actuator of the supercharger
The injection device or turbocharger shall deliver additional air to the cylinders of the propulsion system. The engine management system, which is programmed to prepare the optimum composition of the working mixture, increases the fuel supply. Sor, this composition devots much more energy, which means the power of the engine is increasing.
The speed of the compressor depends on the speed of the engine, so it can be used to ensure that the propulsion system is operating at any given moment.
Rotary compressor unit and operating principle
Regarding the features of rotary compressors, the simplicity of their design, durability and positive dependency between rotors ' speed and changing engine operating modes should be noted.
Air compression is not introduced in the working cavity of the reader, so this type of compressor has been called "with external compression". With equal treatment of the injection and suction pressures, the rotary compressor is reasonably effective; its efficiency is beginning to fall with an increase in intake pressure.
Consists of the rotary compressor from the hull with the two rotors, the two rotors, the two rotors and the synchronizing gears and the pulley.
Rotors have a spiral form. This improves slightly more fluidity and reduces compressor noise. The cline shape of the pressure blower windows contributes to the reduction of the air pressure pulsation. For the same purpose, instead of two-jagged, three jagged rotors are used.
The disadvantages of rotary compressors include strong heating at work, increased noise, pulse pressure and direct relationship between the efficiency of the device and the degree of its sophistication.
Depending on design features, rotary compressors have a positive pressure of 0.5 to 0.6 bar and are widely used in passenger cars.
screw compressor unit and operating principle
The screw-type of the screw type is compact, particularly reliable and high-performance.
The screw compressor has two rotors. They take the shape of a wheel on which the spiral czeal is located with a great angle of inclination. The synchronizing gears on the rotor shaft do not allow contact between the rotors and the hull.
The number of rotor rotors depends on the number of teeth in the gear mounted on the shaft. In the screw compressor, the rotor with ovine is distributable, and the profiles of these are fully consistent with the profile of the rotor rotors.
The screw-type compressors shall provide the diagonal movement of the intake air into the flow part. The speed of rotation of the device makes it possible to significantly reduce the size of the device, and high air pressure allows to install this type of injection device on the fastest and most powerful vehicles.
The main advantages of screw compressors are their balance, reliability and purity of the intake air, which does not have an oil impurities.
However, the complex shape of the rotors and their massage is the reason for the high cost of screw compressors. In addition, internal air compression creates high frequency noise, which is an unmistakable drawback.
The screw compressors have high efficiency-more than 80%-and create pressure around 1 bar.
Consequences of the failure of the injection device
Since the injection device is not part of the main vehicle, but rather a tuning category, the failure of the compressor does not threaten the engine with serious breakage.
Due to reduced fuel cylinder capacity, engine power is reduced. If the part of the compressor is worn out, it must be repaired or replaced.







