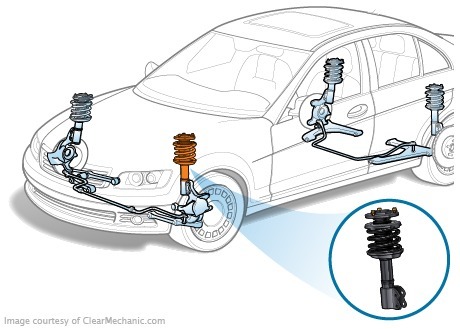
The shock absorbers have been fluctuating in the suspension of the car. If the shock absorbers have failed, the swings of the bodywork after the hit will continue until they cease to dissipate according to the energy dissipation law. Tale of shock absorbers
Tale of shock absorbers
There were no shock absorbers at all. Their role was performed by the springs-the vibration of the body gaced thanks to the friction of the steel plates. But the engineers had to build individual dampers (buffers) for safety and comfort, as the speed of crews grew rapidly over the years. Initially, the constructors presented shock absorbers as a package of compressed friction discs. During the suspension of the suspension, they turned to each other with an effort, absorbing the energy of vibration. But such construcations were quickly worn and overheated. The exit was found in the 1920s. The working body began to use a liquid that prevented excessive vibration of the vehicle from one tank to another through calibrated orifice. In fact, this kind of hydraulic shock absorber can be different shape, but over time telescopic dampers have become very popular. They have a small mass, compact dimensions, and at the same time have high reliability and excellent cooling. Such designs are installed on vehicles and today.
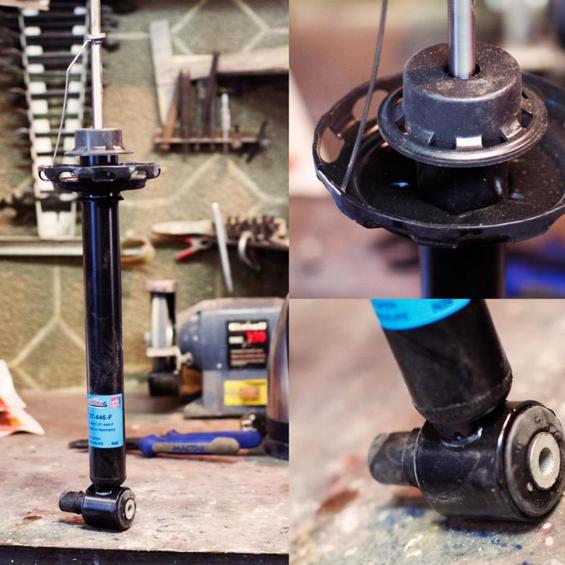

single-tube dampenes
Single-tube dampens are a single cylinder. The volume of the shock absorber shall be compensated by a gas chamber which is separated from the liquid by a special floating piston (sometimes membrane). Such shock absorbers are therefore called gas or gas-filled. Single-wall shock absorbers are perfectly cooled, and consequently their useful life is increasing. Therefore, "single-mouthhanders" are often used in sports cars. In such shock absorbers, oil is under extremely high pressure (up to 30 atmosphes) and no contact with air, which is why the probability of forming harmful emulsion is reduced to zero. Thus, any provision is suitable for the installation of such a damper. But the gas shock absorbers have drawbacks. The first and most important is the low efficiency when compared to two-pipe, since the intake valves and openings are only on piston, and therefore their quantity and diameter are limited by its size. And the other damper dames are afraid of the damage. For example, if a stone from the road hits the wall of the cylinder, then the piston may be curable.
Double-pipe dumping
They consist of two cylinders which have one in another. In the inner cylinder, filled with oil, the piston shall be moved, which is bound with the suspension lever or bodywork. The external cavity is a compensation volume, where the "needless" liquid is removed. The swings shall be made by friction between the oil and through the calibration valves and openings located at the bottom of the inner cylinder and piston. This device is considered classic. The design is efficient, simple and reliable, and the main cheap from proven technology of manufacture. But lately, "two-panties" are rare. The main reason for this unpopularity is frequent overheating. The double walls block the cooling (the thermos effect), and the oil can boil fast on rough roads and the shock absorber ceases to function. This is further facilitated by the exposure of the air to the working fluid in the outer cylinder. Due to the increase in temperature, it forms a substance that degrade oil properties. Therefore, "two-tubers" are not placed above 45 degrees, and this often makes it difficult to install them.
Combinations of damper
These shock absorbers have been gaining popularity since they are a great compromise if you are talking about two previous devices. Combined models are considered reliable, accessible and highly efficient. Their structure resembles a double-tube shock absorber. The only difference is that in an outside cylinder the gas is injected pressurized to 3 atmosfr, which does not give the working liquid to be boiled.









