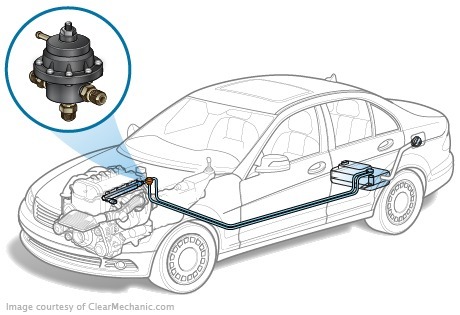
In the engine power system, the fuel pressure regulator shall be used to maintain the constant pressure in the fuel rail. The pressure level must always be higher than the intake manifold, otherwise the nozzle will simply not be able to enter the fuel collector.
The malfunction of the regulator is able to relieve the pressure in one night, and in the morning the engine starts with great difficulty
The intake manifold changes are changing depending on the engine speed and when they are reduced or increased, the pressure reducer synchronously changes the pressure in the fuel rail.
Design of the pressure regulator and the principle of its work
The regulator is located inside a solid steel body, which must withstand high pressure. The control mechanism shall consist of a diaphragm and a non-return valve preventing the return of the fuel under pressure back to the mainline. The valve is connected to the diaphragm actuating the pressure of the fuel ramp on the one side and the valve spring. At the moment of injection, the pressure falls because the fuel through the nozzle is left in the intake manifold. Vacation created in the suction pipe also affects the membrane.
Modes of operation of the pressure regulator
The lower the intake manifold, the greater the pressure of the ramp.
The primary operating mode for the pressure regulator shall be idle. At the time of operation, the vacuum is idle reaching the lowest point and the pressure in the fuel rail is the highest point. This value shall be placed on the pressure control body for the control of the supply system.
Pressure regulator not to be repaired, and in case of malfunction need to be replaced
In full load in the suction pipes, the vacuum is increased and the pressure regulator reduces the supply of the fuel.
Irrespective of the engine operating modes, the pressure regulator shall always react accurately to its changes. In order to be able to compensate in any mode, the fuel pump shall always be pressurized.
Committing fuel pressure
The fuel pressure regulator is closed at the time the ignition is switched off, and the fuel supply piping is kept under pressure for an extended period of time. In this condition, the non-return valve in the fuel pump is also closed, contributing to maintaining the pressure throughout the fuel supply system. This is necessary so that the engine can be started immediately after a long parking lot without waiting for the pump to lift the pressure.
Characteristics of the pressure regulator
Valve wedge
The valve shall be periodically broken in the event of this malfunction. When the valve is wedge, the fuel is "ramp" to the valve. If the valve is suddenly activated, the fuel goes off the open line back into the tank. It is not possible to predict the behavior of the pressure regulator of any electronic device, so the engine is not stable.
Valve spell
The valve is permanently closed, leading to a sharp increase in pressure. For example, instead of 2.5 kg/cm2, the ramp will be 3...5 kg/cm2 or more. The increase in the average pressure will result in a sharp increase in the performance of the nozzles that will constantly work at the capacity limit. The result would be an explosion of fuel-air mixture.
Fuel rail pressure diagnostic is performed by a pressure gauge that connects to a special diagnostic device
As the amount of air remains the same, the fuel will not burn completely. As a result, there will be cotton in the exhaust system, smoke clubs from the tailpipe and a change in the dynamics of the engine acceleration.
The valve is "not holding"
In the event of a total failure of the valve, the fuel begins to circulate freely through the fuel line, continually returning to the tank. Fuel pressure falls to the limit. This valve malfunction shall be affected by all engine operating modes, as the injectors start to operate at the lower end of the performance.
A sharp fall in engine power is a symptom of the valve failure. At the time of acceleration the intake manifold vacuum increases, resulting in an increase in the replacement air flow. At this point, the regulator must increase pressure to make more fuel available in the nozzle, but this does not happen, and the mixture abruptly.
Effect of the failure of the governor of the engine
The failure of the pressure regulator's valve is reflected not only at work, but also at engine starting. If the regulator is operating, the pressure in the fuel rail does not fall after the engine is stopped. If the valve is bad, the pressure will drop during parking.
After ignition on, the engine will not start until the pump fills the system. Only after the pressure is closer to the desired level, the first "flashes" will appear. If there is enough battery power, the engine may be able to start.
In addition, there will be an unstable idle, gas failure during acceleration and a general fall in engine power.







