The internal combustion engine should have become an alternative to the industrial steam engine, but the inventor-enthusiasts immediately felt its potential. They were able to find a way to increase the power of the engine without increasing its mass. Otto, who created the first four-stroke engine in history, played a key role in this. History of the engine of Otto
History of the engine of Otto
The motor, designed by the inventor Alphonse Boe de Rocha and embodied in the metal by German Nikolaus Otto in 1867, was, at times, perfect. It was cheap in operation, compact and did not require constant control. The engine worked on a special algorithm widely known today as "Otto cycle." In 1875, Otto was producing more than 600 engines a year.
It was Gottlieb Daimler and his fellow engineers drew the attention of Nikolaus Otto to the advantages of four-stroke
Otto worked as a talented engineer named Gottlieb Daimler, who was burnished by the idea of building a car. Nikolaus Otto did not consider it necessary to improve the existing engine, and Daimler, who was able to use the motor in the car design, had to leave. Together with a like-minded man named Karl Benz, in 1889 Daimler managed to create the first car with petrol four-stroke internal combustion engine running on Otto cycle.
What is the engine's "ticks"?
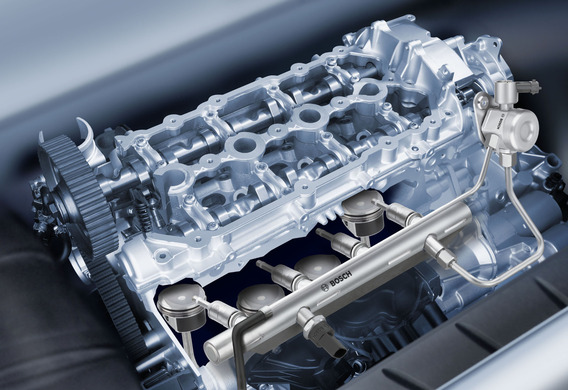
The four-stroke engine is different from two stroke, that the gas distribution has separate phases of the intake and release. The valves are located in the head of the intake cylinder head and vent valve, respectively. They are opened with the help of the engine crankshaft.
The first step is called "Intake." At this point, the piston begins to move down from the top of the dead point, creating a discharge. At the same time, the intake valve opens and the fuel air mixture is sucked into the cylinder. When the piston returns to the bottom of the dead point, the valve is closed and the intake phase is terminated.
A single dose of fuel at a certain point at the current stage of development of four-stroke engines ceased to be a dogma
The second tick is called compression. The piston starts upward, both valves are closed. At that moment the fuel mixture is compressed and heated. This is necessary for the more complete and efficient combustion of fuel.
The third tick is the "work move". A spark of ignition (or compression, if it is a diesel engine) ignites a fuel-air mixture slightly. At this point, the gases are rapidly expanding, and the piston is very much lower, thus making useful work.
The fourth bar is called a "release". When the piston has made a working stroke and is in the lower dead point and the exhaust gas from the cylinder is to be removed, the valve shall be opened. Through it, the pistons beginning to move up, the exhaust gases exhaust.
Diesel engine operating procedures differ only in that the compression of the cylinder is only air, and the fuel is charged to the combustion chamber at the end of the compression with the help of the nozzle.
New Mechanisms-Old Principle
From the moment of invention and up to our days engineers have constantly perfects the four-stroke engine. Most of the innovations were in the gas distribution mechanism. For example, if the cylinder earlier had only two valves, the number of modern motor-valves was up to five. In addition, many manufacturers use valve timing systems. The most famous are VVT-i from Toyota and Valvetronic from BMW. The variable phase system allows the valve rise time and height to be changed, depending on the engine operating modes.
After 150 years, the principle called the Otto cycle remains valid. Physicists argue that a new kind of fuel is needed for further progress
The nutrition system has also changed. Practically on all modern engines, the carburettor gave way to distributed fuel injection. Ignition, dosage, and fuel feed is now in charge of electronics.
The incoming air is increasingly used for better cylinder capacity. Increasing the density of the air in the cylinders allows to get a powerful engine with a relatively small engine capacity and reduce fuel consumption. For example, an engine 1.4 TFSI from a double turbocharged "returns" of 185 hp.
In the last two decades diesel vehicles have been popular. If the engines of heavy fuel used to be exclusively for trucks and buses, now more than 50% of the cars sold in Europe are in the "solyrak". Dizay is more economical than its petrol brethren, and if the engine is equal to the engine, they have a much larger torque and give the car a decent dynamic. To date, almost all diesel engines are turbocharged.
Advantage and disadvantages of four-stroke engines
The most important of all the engines running on the Ottovo cycle. In addition, four-stroke engines are relatively silent, and the use of catalytic converters also makes them more environmentally friendly.
The reliability of four-stroke engines is an undeniable advantage. The resource of passenger cars is up to half a million kilometers, and it's not the limit.
The disadvantages of modern motors are found in their complex technical device. They are expensive in production, and they are very demanding in terms of fuel and oil quality. Repairs to their forces in the field, without special tools and skills, are virtually impossible.
Operation of four-stroke engines
In the first place, the selection of petrol stations should be carefully chosen. Fuel systems, especially diesel vehicles, are poorly "digestied" by poor fuel. Moreover, a single refueling station "left" can disable a catalyst. And his replacement could turn into "cost."
The development of microprocessor management of four-stroke processes resulted in human intervention not required for years
Most of the failures of modern engines are not directly related to mechanical parts. Defective problems tend to occur in "weak spots", in the air supply system or in electrical equipment. As a result of the complexity and development of microprocessor management systems, it is virtually impossible to diagnose the problem without a diagnostic computer.
The engine is the main and most expensive part of the car. Therefore, in the event of a breakdown, the repair is better entrusted to the service center, avoiding the "garage" specialists.







